
2020-05-28
1122
原创
list的元素的自然排序
方式一:
- 将list的集合取出来放到TreeSet当中进行排序,然后根据排序顺序取出放置到list集合当中
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<Integer>();list.add(3);
list.add(2);
list.add(4);
TreeSet ts=new TreeSet((o, t1) -> (int)o-(int)t1);
ts=new TreeSet(list);
System.out.println(ts);
方式二:
- 将list的集合转换为数组,使用数组的排序规则进行排序
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(3);
list.add(2);
list.add(4);
Integer[] Integers = new Integer[list.size()];
Integer[] c=list.toArray(Integers);
Arrays.sort(c);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(c));
方式三:
- 使用集合的工具Collections的sort进行排序
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<Integer>();
Collections.sort(list);
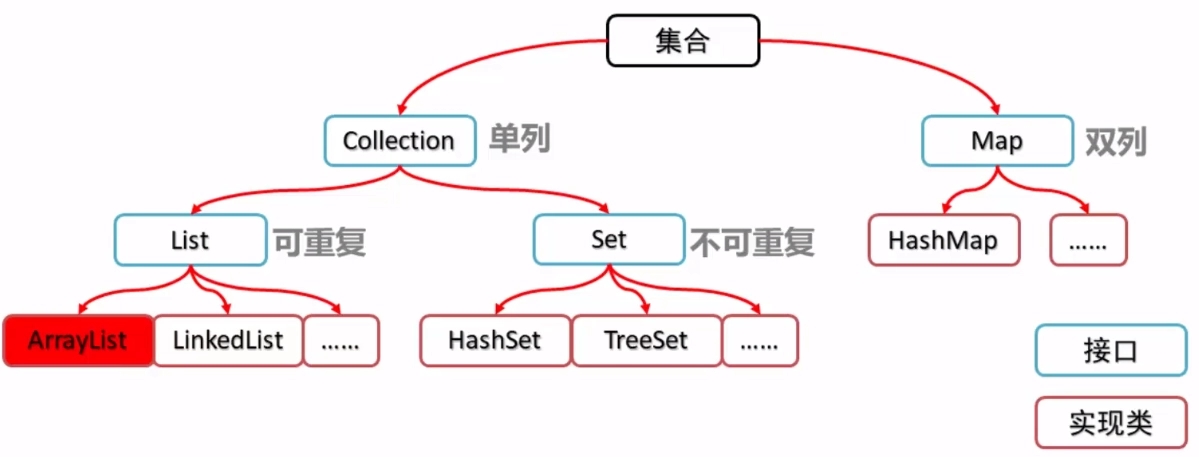
Collections:针对集合操作的工具类,都是静态方法
Collections和Collection的区别?
Collections:是集合进行工具操作的类,比如集合排序二分查找等等
Collection:是单列集合的父类,有List和Set的子接口
java
Spring